L. Cheng, I. Maruyama, A Prediction Method for the Corrosion Rate of Steel Rebar in Carbonated Mortar under Variable Environmental Conditions, J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 21 (2023) 611?630.
こちら、中性化したモルタル(コンクリート)内で生じる鉄筋の腐食反応速度を評価する手法を膨大な実験から新たに提案しました。といっても、結局、鉄筋腐食はほとんどの場合で鉄筋周囲のモルタルの電気抵抗で律速されてしまうので、シンプルになってしまうわけですが。
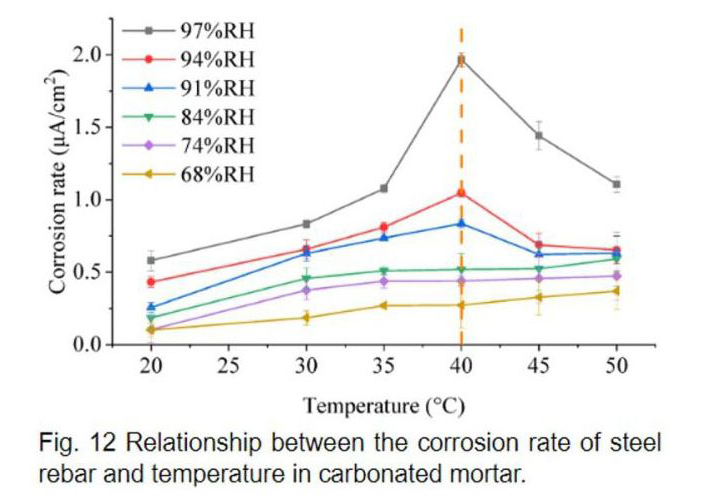
モルタルの電気抵抗の温湿度依存性を厳密に実験で評価した点、および、かぶり厚さによって変化する腐食速度律速プロセスの評価の方法は、いろいろ便利につかってもらえると思います。データだけでも見てほしいです。指針類につかいたくなる図が多いと思います。
日本総合試験所さんと自治体のご好意で実建物3件について検証した事例もついています。
昨今、RC建築物の残余寿命評価などがおこなわれていいますが、科学的根拠の少ない工学式やよくわからない丸めた式で評価せざるを得ない状況が多いので、そのあたりを変えていきたいと考えています。といっても、この論文の中も実験式が多く、もう一段、電気抵抗の観点での分析と空隙構造の関係を今後はしっかりやりたいと思っています。
Here, we have proposed a new method to evaluate the corrosion reaction rate of reinforcing steel bars that occur in the carbonated mortar (concrete) based on the parametric study of the corrosion rate of carbon steel in the carbonated mortar with different temperatures, equilibrium RH, and different cover depths. It is pretty simple, because the corrosion of reinforcing steel bars is, in most cases, rate-limited by the electrical resistance of the mortar around the reinforcing steel bars. I think that the dependence of the electrical resistance of the mortar on temperature and humidity was evaluated rigorously in the experiment, and these data could be useful for you. The paper also includes case studies of three actual buildings, courtesy of the Japan Testing Laboratory and the local government. Recently, an evaluation of the remaining service life of RC buildings has been conducted, but in many cases, the evaluation has to be based on empirical formulas with a bit little scientific basis. I hope our results contribute to this business.